1. Introduction to a Healthy Diet
A healthy diet is not about strict limitations or staying unrealistically thin. Instead, it’s about feeling good, having more energy, and improving your health. The foundation of a balanced diet includes proper portions, a variety of foods, and understanding the role of each macron1utrient and micronutrient.
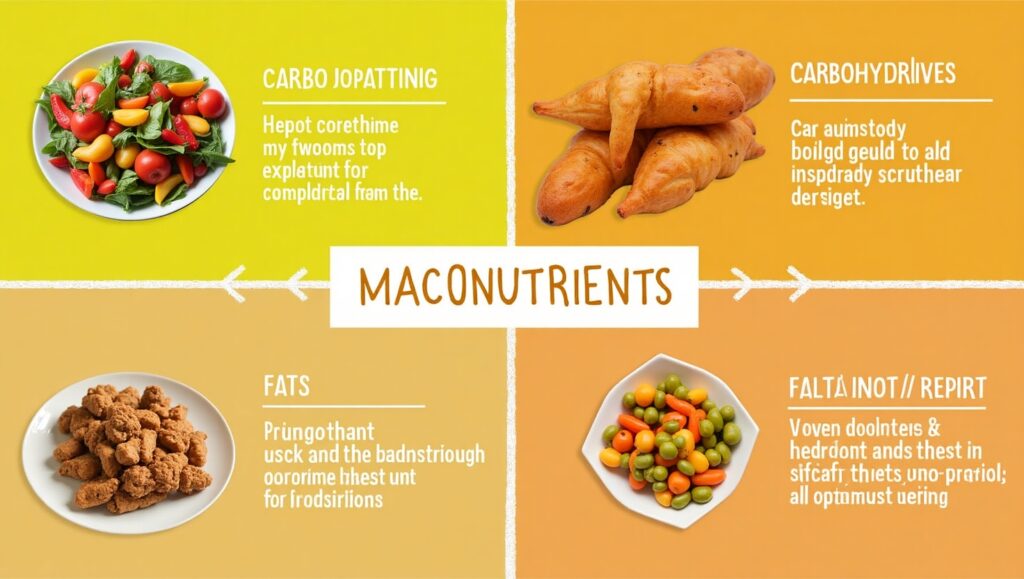
2. Understanding Macronutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats
Macronutrients are essential for energy and bodily functions. Carbohydrates are the body’s main energy source, proteins build and repair tissues, and fats support cell structure and hormone production. Understanding these macronutrients and how to balance them in your diet is crucial for optimal health.
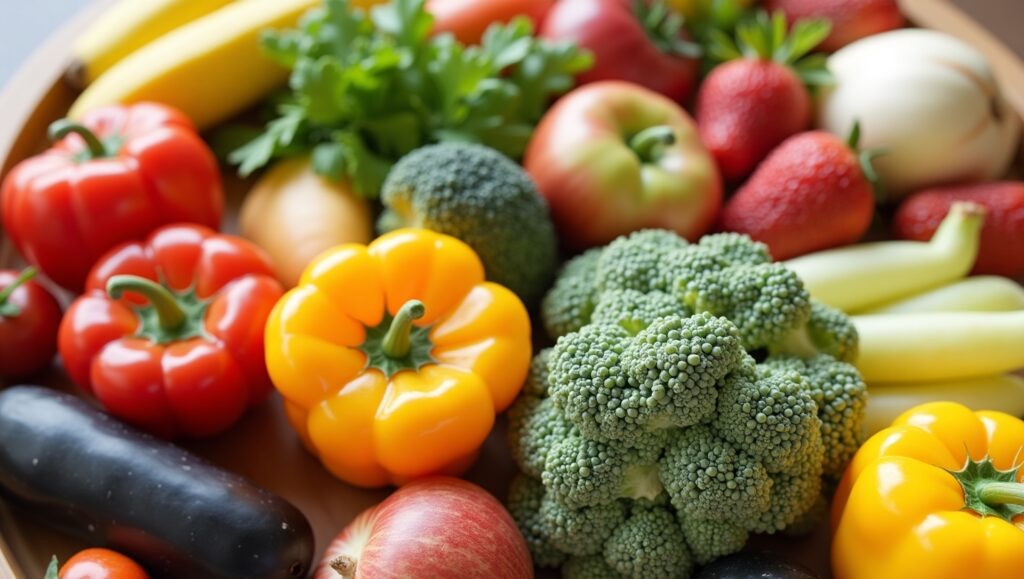

3. Importance of Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals
While macronutrients provide energy, micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals play vital roles in various body functions, such as immune health, bone strength, and wound healing. Ensure a diverse diet that includes a variety of colorful fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to meet micronutrient needs.

4. The Role of Fiber in a Healthy Diet
Fiber is vital for digestive health, helping regulate bowel movements and reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease. Including high-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains helps maintain gut health and control blood sugar levels.
5. Hydration: The Often Overlooked Nutrient
Water is essential for almost all bodily functions, from nutrient absorption to temperature regulation. Staying hydrated is crucial for digestion, metabolism, and overall well-being. Aim for at least 8 cups (2 liters) of water per day, adjusting based on activity levels and climate.

6. How to Plan a Balanced Plate
A balanced plate should contain a variety of food groups: half should be fruits and vegetables, a quarter should be lean protein, and a quarter should be whole grains. This ensures that you get a variety of nutrients without https://www.thedietguide.xyz/ adding on any one food group
7. Whole Foods
Whole foods are less processed and retain more of their nutritional value. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and healthy fats. Processed foods, on the other hand, often contain excess salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats, contributing to obesity, heart disease, and otherhttps://goodhealth.co.nz/ health problems.

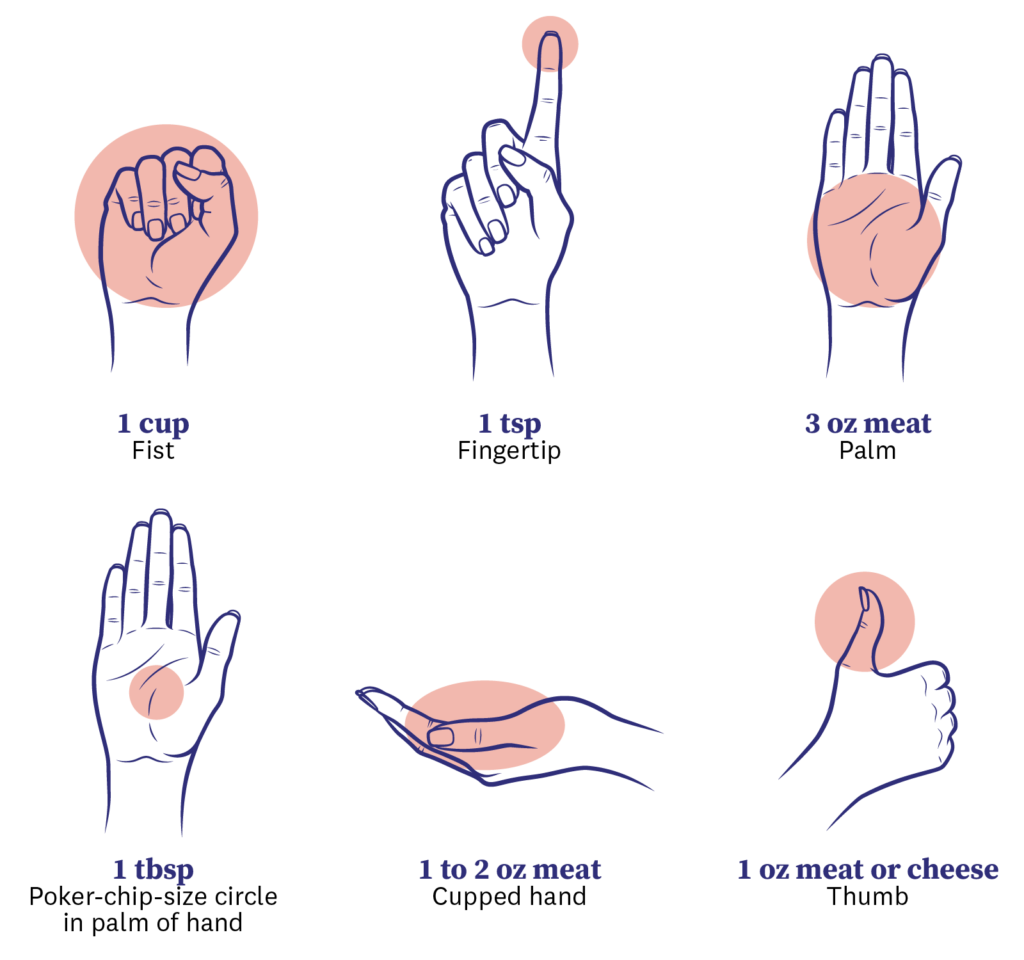
8. Understanding Portion Control
Portion control is essential for weight management. Eating appropriate portion sizes helps prevent overeating and promotes a healthy balance of calories. Using smaller plates, reading nutrition labels, and listening to your body’s hunger cues can help maintain portion control.
9. The Importance of Eating Regular Meals
Regular meal times help stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent overeating later in the day. Skipping meals can lead to unhealthy food choices and overeating. It’s important to have three balanced meals per day, with healthy snacks in between if needed.

10. The Role of Healthy Fats in a Diet
Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, are important for maintaining heart health, supporting brain function, and providing energy. Try to replace unhealthy trans fats and saturated fats with these healthier alternatives.
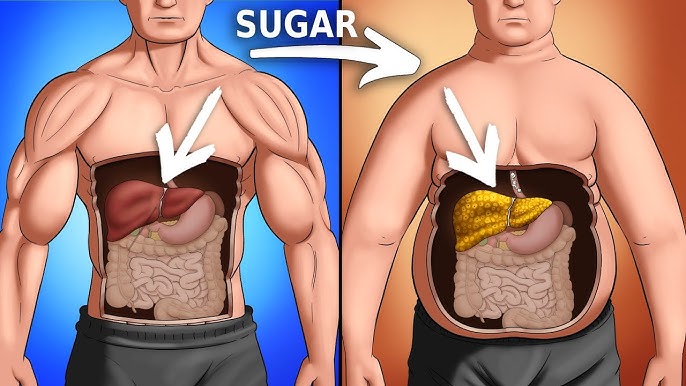
11. The Impact of Sugar on Your Diet
Excessive sugar consumption is linked to weight gain, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Reducing sugar intake, especially added sugars in beverages, snacks, and processed foods, can have significant health benefits.
12. Reducing Salt Intake for Better Health
High salt intake is a major contributor to high blood pressure and heart disease. Aim to limit processed foods, which are typically high in sodium, and use herbs and spices to add flavor to your meals instead of salt.

13. The Role of Protein in Building Muscle and Repairing Cells
Protein is essential for building and repairing muscle tissues, particularly after exercise. It’s also important for maintaining healthy hair, skin, and nails. Sources of lean protein include poultry, fish, beans, lentils, and tofu.
14. Plant-Based Diets: Health Benefits and Considerations
Plant-based diets, which emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and plant proteins, have been associated with lower risks of heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. However, it’s important to ensure adequate intake of protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12.
15. Eating for Weight Management
When aiming for weight management, it’s important to focus on nutrient-dense foods and balanced portions rather than restricting entire food groups. Integrating lean proteins, whole grains, and plenty of vegetables helps control hunger and maintain energy levels.
16. Snacking: Choosing Healthy Options
Healthy snacks can be part of a balanced diet when chosen wisely. Opt for whole foods like fruits, vegetables, nuts, and yogurt. Avoid processed snacks that are high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, as these can contribute to weight gain and health issues.
17. The Impact of Alcohol on Your Diet
Alcoholic beverages can add unnecessary calories to your diet without providing nutritional value. Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with nutrient absorption, liver function, and lead to unhealthy eating habits. Moderation is key.
18. Customizing Your Diet for Activity Levels
Your diet should be tailored to your activity level. Athletes or those who engage in regular intense exercise may require more protein, carbohydrates, and calories to support muscle recovery and energy. On the other hand, sedentary individuals may need fewer calories.
19. Special Diets: Gluten-Free, Keto, and Vegan
There are many specialized diets, each with its own set of benefits and considerations. Gluten-free diets are essential for those with celiac disease, while a keto diet may help those looking for weight loss or better blood sugar control. Vegan diets, if well-planned, can provide all essential nutrients while promoting health.
20. Listening to Your Body: The Key to Long-Term Success
Finally, it’s crucial to listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues. Eating mindfully, enjoying your meals, and avoiding restrictive diets that create unhealthy food relationships are vital for maintaining a long-term healthy eating pattern.
FAQ: how to diet in 2025?
1. What is a balanced diet?
A balanced diet includes a variety of foods from all food groups: fruits, vegetables, whole grains, proteins, and healthy fats. It provides essential nutrients—vitamins, minerals, fiber, protein, and healthy fats—while controlling calorie intake to maintain optimal health.
2. How many meals should I eat a day?
Most people should aim for three balanced meals a day, with healthy snacks in between if needed. Regular meals help maintain energy levels and prevent overeating. The frequency of meals can vary based on individual needs and goals.
3. How can I reduce sugar in my diet?
To reduce sugar, limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and snacks. Opt for natural sweeteners like fruit, and check food labels for added sugars. Eating whole foods such as vegetables, fruits, and whole grains helps control sugar intake while providing essential nutrients.
4. What are some healthy snack options?
Healthy snack options include nuts, seeds, fresh fruit, vegetables with hummus, yogurt, and whole-grain crackers with cheese. These snacks provide a balance of fiber, protein, and healthy fats that keep you satisfied between meals.
5. Is it necessary to take supplements if I eat a balanced diet?
If you eat a well-rounded diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, you may not need supplements. However, some individuals may require specific supplements, such as vitamin D, vitamin B12, or omega-3, depending on their diet and health conditions.
6. How do I maintain a healthy weight with my diet?
Maintaining a healthy weight involves balancing calorie intake with physical activity. Focus on eating nutrient-dense foods, avoiding empty calories from processed foods, and paying attention to portion sizes. Regular exercise and a healthy relationship with food also play key roles in weight management.
7. Can I lose weight by cutting out carbs completely?
Carbohydrates are an important part of a balanced diet, providing energy for the body. Cutting out carbs entirely can be unsustainable and lead to nutrient deficiencies. A better approach is to focus on healthy carbs like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, and avoid refined carbs like white bread and sugary snacks.
8. What is the role of fats in a healthy diet?
Healthy fats, such as those from avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, play a vital role in hormone production, brain function, and cell structure. They also help absorb fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). It’s important to focus on unsaturated fats while limiting saturated and trans fats.
9. How can I make my diet more plant-based?
To transition to a more plant-based diet, start by increasing your intake of fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. Replace animal proteins with plant proteins like tofu, tempeh, and lentils. Be sure to include a variety of foods to meet all nutrient needs, especially for vitamin B12, iron, and calcium.
10. Is it okay to eat out while maintaining a healthy diet?
Yes, it is possible to eat out and still maintain a healthy diet. opts for grilled, baked, or steamed options instead of fried foods. Ask for dressings and sauces on the side, and choose whole grain options when available. Many restaurants offer healthier choices, and being mindful of portion sizes can help you stay on track.